Optimizing Last-Mile Delivery During a Driver Shortage
The last mile is getting more attention in this era of eCommerce sales increases, smaller order sizes, and larger overall shipment volumes. Not only is this supply chain gap notoriously difficult for companies to close, but finding qualified drivers is currently a major concern. An expensive link in the supply chain, the last mile can account for over 50% of shipping costs for the average order.
Managing On-Demand Crowdsourced Delivery
According to the American Trucking Associations (ATA), the current driver shortage stands at 80,000 and may reach 160,000 by 2030. And with the national unemployment rate hovering at a 50-year low, attracting and retaining new drivers is more difficult than ever in this constrained labor environment.
As a result, companies are turning to on-demand, crowdsourced delivery providers that specialize in ultrafast last-mile shipments—usually same-day or next-day, and often within just a few hours. Taking this step helps both B2B and B2C companies leverage existing last-mile networks, such as Lyft, Uber, DoorDash, and Postmates, without investing in additional drivers, vehicles, and shipping infrastructure.
An auto parts store or apparel retailer that can’t meet a customer’s delivery requirement may lose out to competitors who have their own last-mile logistics infrastructure in place. “By calling in an on-demand, crowdsourced delivery provider, companies can expand their delivery options,” says David Ward, Director of Strategic Partnerships at Elite EXTRA, “and use quick delivery times to stay in their customers’ good graces.”
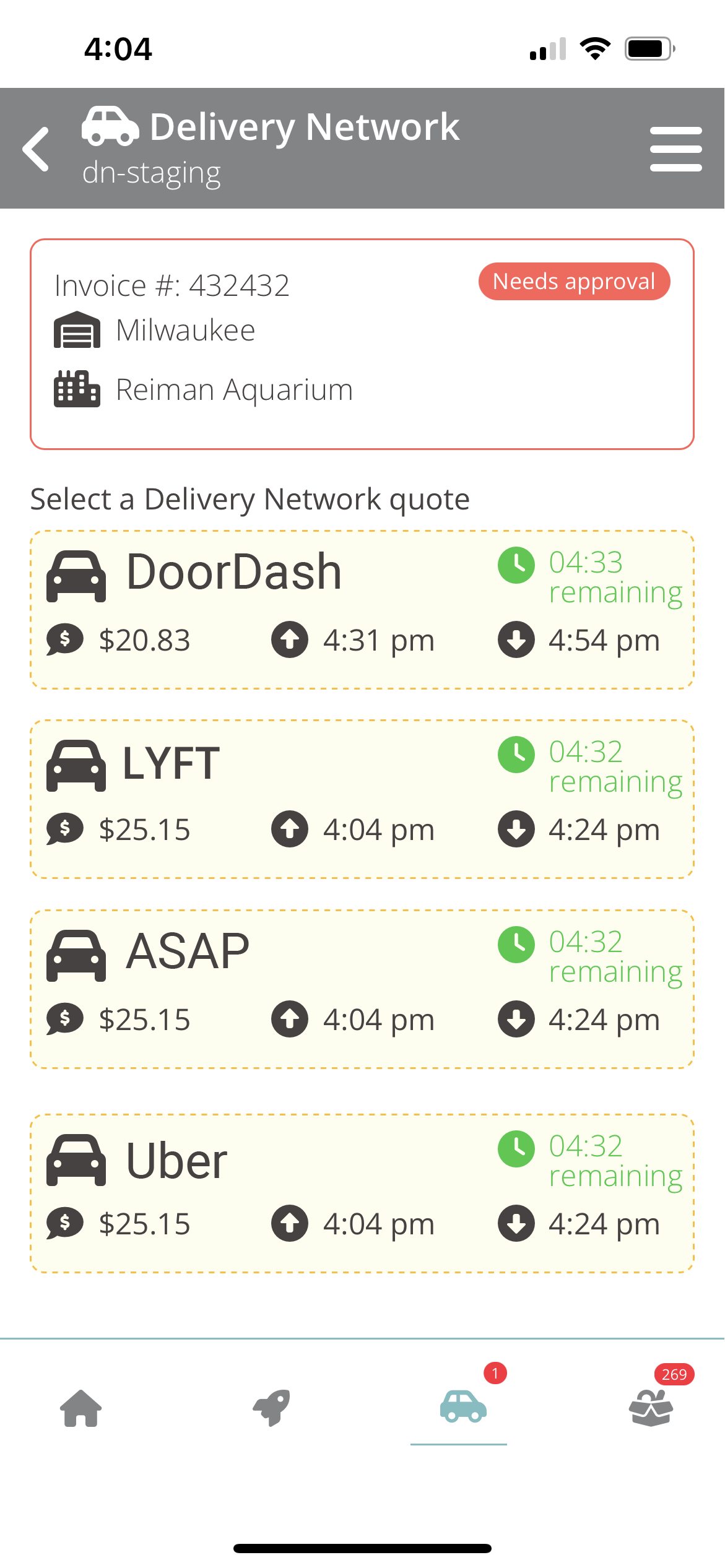
Elite EXTRA, a Panasonic Connect partner company whose software helps businesses reduce local delivery times and expenses, gives companies a tool for shopping the prices and available delivery windows of numerous third-party crowdsourced providers. Installed on a Panasonic TOUGHBOOK computer, the Delivery Network app helps organizations choose the best option for every order.
Pairing TOUGHBOOK devices with Delivery Network helps companies that would otherwise have to manage multiple last-mile providers for each individual order. Each provider has full control over its network, pricing, and availability, allowing them to shop across all on-demand options—without having to contact each one individually.
“If Lyft is surge pricing right at the time you need to get a delivery out the door,” Ward explains, “you may wind up paying quite a bit more than you would if you had multiple options to choose from.”
Streamlining the Last Mile
Delivery Network automates the contracting and billing transactions that take place between the company and its crowdsourced delivery networks. Featuring built-in integrations with most last-mile delivery networks, the platform automates communications with those delivery fleets, taking manual input out of the equation altogether.
And because on-demand delivery services employ drivers who use their own devices when receiving, transporting, and delivering orders to end customers, equipping them with the mobile manager app speeds up the scanning, receiving, routing, and delivering processes.
“We fill the middleman role between a company’s point-of-sale system and the individual crowdsourced fleets,” says Ward. Delivery Network provides the best available crowdsourced delivery options for each order and across all manufacturer, retailer or distributor locations. This helps companies seamlessly tackle their final-mile delivery challenges.
An Insurance Policy Against Uncertainty
Installed on Panasonic TOUGHBOOK devices, Delivery Network gives warehouse and DC managers a powerful tool to get deliveries out the door fast. Managers use the devices while walking around the warehouse, while pickers and forklift drivers rely on them while moving about and pulling orders for delivery.
“Panasonic gives companies an ‘insurance policy’ in a device that’s survivable, securable, and durable enough to survive in extremely harsh work environments,” says Jim Dempsey, director of U.S. business development and partnerships at Panasonic Connect North America. “We’re the safeguard that ensures that applications like Delivery Network stay up and running as close to 100% of the time as possible.”
One big-box office products retailer began using Delivery Network to leverage the power of crowdsourced last-mile delivery providers. At some locations, the company has completely replaced its driver fleet with crowdsourced options. This eliminated overhead and also effectively solved the company’s driver shortage.
“For this particular retailer, it made more sense to get rid of their vehicles and last-mile assets and leverage the crowdsourced model,” says Ward. The company has also significantly reduced its hardware costs by using TOUGHBOOK devices, which can withstand anything the warehousing, distribution, and delivery environment puts in front of them.
“The company is at a point where less than 1% of its TOUGHBOOK devices have needed repair or replacement,” Ward adds. “That’s vastly below any other hardware the office supply retailer is using in its operations.”
Using Automation to Manage Complexity
With U.S. eCommerce sales crossing the $1 trillion threshold for the first time in 2022—a milestone that wasn’t expected to happen until 2024—companies continue to look for innovative ways to fill their last-mile gaps. Higher transportation costs, the escalating driver shortage, and the rising costs of doing business make running a final-mile logistics operation cost-prohibitive and resource-intensive.
Panasonic Connect and Elite EXTRA offer a combined solution so companies can meet customer demand for fast delivery and compete effectively in the market.
Both B2B and B2C businesses are being asked to deliver orders faster than ever in an environment where labor and fuel are the biggest costs of doing business. Using automation, companies can optimize the last mile of their supply chains, save money, and more effectively manage new complexities as those challenges arise.
Follow this link to learn more about Panasonic Connect solutions for transportation operations.
![]()